Wat is FFC?
FFC is an abbreviation for Flat Flexible Cable. Flat Flexible Cable (FFC) is a flexible cable that provides 1:1 connection between devices. They are composed of multiple flat wires placed in parallel and covered with protective shielding tape. This makes these cables an excellent choice for projects that require quick connections or high-flex applications where the cable needs to be bent repeatedly without breaking.
FFC Type:
There are two main types of FFC, each with a different contact or pin layout. Both types go by various names, but the most common are Type A and Type D.
Type A (also called Type 1, Type BD, or Same Side): Each end of the cable has a row of pins, with both pins on the same side of the FFC surface. This is the most commonly used type of FFC.

(Type A FFC)
Type D (also called Type 2, Type AD, or Opposite Side): Each end of the cable has a row of pins, with one on the top of the FFC and one on the bottom. This type of FFC is less common and is typically used in special case applications, such as connecting a device with a standard pin layout to a device with a reversed pin layout.

(Type D FFC)
Components of FFC:
Wire: A flat conductive path that carries electrical signals between devices connected by an FFC.
Pins: Individual conductive contact points at each end of an FPC that connect to corresponding pins on another device.
Pitch: The distance between the centers of two adjacent pins. The size of the pitch determines the compatibility of the cable with the connector.
Support tape: A reinforcement layer added to the end of an FFC to make it easier to insert into the connector without damage.
Composition of FFC
FFC is made of a row of flat wires made of copper and tinned at both ends. A flexible polyester material is covered around the row of wires to insulate and protect the conductors. Each end of the cable has rectangular reinforcement ribs, usually made of a thicker polyester material.
How FFC works
The FFC is designed to connect to the devices on both ends with a 1:1 connection, which means that each pin on one end of the FFC corresponds exactly to the same numbered pin on the connected device. Once the FFC is properly connected to the devices on both ends, electrical signals are able to be transmitted from one device through the conductors of the FFC to the other. This connection allows two devices to communicate when connected to the FFC and a power source.
Advantages of FFC:
High Flexibility: The flexible material contained in FFCs makes them suitable for applications that require frequent movement.
Quick Setup: The simple process of setting up FFCs between devices allows for quick connection and disconnection.
High Versatility: The function of FFCs is to create a 1:1 connection between devices, which means that the cable can be easily reused in any other project that requires a 1:1 connection.
Cost-Effectiveness: FFCs are generally produced at a lower cost than FPCs, so they can be purchased at a lower cost.
Disadvantages of FFC:
Limited complexity: FFCs cannot support the same level of circuit complexity as FPCs, so they are less suitable for advanced functional requirements.
Durability: FFCs may not be as durable as FPCs in harsh environments.
Common uses of FFC:
Cameras: In cameras, FFCs connect image sensors to processing boards to transfer high-resolution image data.
Robotics: FFCs are often used in mobile robotic parts, such as robotic arms, to form flexible joints and allow for a wide range of motion.
Consumer electronics: FFCs are used to connect components in everyday devices such as laptops, printers, and monitors.
Automotive: Instrument panels, infotainment systems, and other in-vehicle electronics use FFCs to make simple connections within the system.
Medical devices: FFCs are incorporated into imaging devices and diagnostic machines used within the medical space.
Industrial equipment: Industrial robots and automation systems utilize FFCs to connect many components throughout the machine.
Home appliances: FFCs are used in home appliances such as washing machines, microwave ovens, and other household appliances.
FPC: Flexible Printed Circuit
A flexible printed circuit (FPC) is a flexible cable that has circuitry printed onto a flexible substrate. These flexible printed circuit cables can be bent and folded, allowing for complex electronic connections in tight spaces. FPCs perform the same functions as traditional printed circuit boards (PCBs), but on a flexible surface.
Printed on top of the FPC is a highly customizable circuit, so each FPC is typically designed for a specific application. Their flexible and lightweight construction makes them best suited for projects that require more complex connections in limited space.
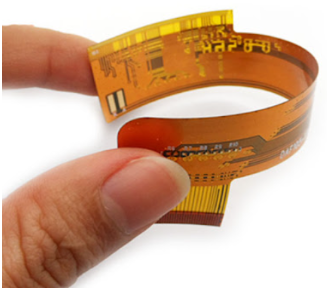
Components of FPC:
Pins: Individual conductive contact points at either end of an FPC that connect to corresponding pins on another device.
Pinout: The arrangement of pins on an FPC. Pinout ensures proper alignment for signal transmission.
Pitch: The distance between the centers of two adjacent pins. Pitch determines cable compatibility with connectors.
Vias: Plated holes that allow electrical connections between different layers of an FPC.
Electrical traces: Paths that carry electrical signals on an FPC. An FPC can consist of one or more layers of conductive traces.
Electrical components: Various devices mounted on an FPC, including resistors, capacitors, integrated circuits, and transistors.
Ribs: Rigid components added to certain areas of an FPC to provide additional support, especially at connection points.
Substrate: The base material of an FPC that provides flexibility and support for conductive traces.
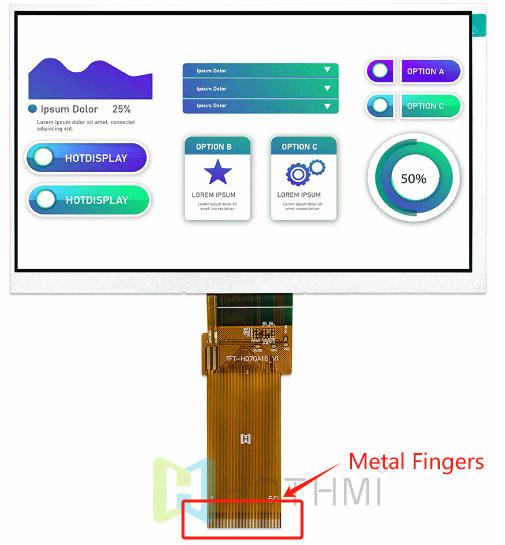
(FPC与显示屏的连接)
Composition of FPC
The construction of an FPC begins with a flexible base layer made of polyimide or polyester. On top of this base layer, one or more layers of conductive traces made of copper are bonded above each layer using acrylic or epoxy adhesives. Multilayer FPCs have through-hole vias that are coated with copper on the inside and ends to allow the layers to interact with each other.
Throughout the FPC, certain areas may use thin polyimide-based stiffeners or thicker stiffeners made of fiberglass-reinforced epoxy to provide varying degrees of additional support.
On top of that, the polyimide cover provides insulation and protection. FPCs may also feature shielding made of aluminum or copper foil on certain sections of the cable to prevent EMI. Both ends of the cable have tinned or gold-plated pins for easy soldering.
How FPC works
Similar to an FFC, an FPC has a row of pins on each end that connect to different devices on each side. When connected to a power source, the two devices can communicate with each other by sending electrical signals from one device to the other through the FPC.
Unlike an FFC, electrical signals travel through the FPC in a more complex path along traces etched on the FPC. Some signals also travel directly to certain mounted components, rather than passing directly through to reach the device on the other end. In a multilayer FPC, each layer of routing is separated so that signals can reach other layers through the conductive exterior of the vias.
Advantages of FPC:
High complexity: FPCs are able to support complex circuit designs, including multiple layers and surface mount components.
High customization: With the ability to incorporate countless versions of circuit designs in multiple layers and attach other components, FPCs can be highly customized to provide specific functionality to meet the needs of specific applications.
High flexibility: The flexible material that serves as the basis of the cable allows FPCs to perform well in applications that require frequent movement.
Strong durability: FPCs are generally more resistant to harsh conditions, such as high temperatures and exposure to chemicals, than FFCs.
Disadvantages of FPC:
Higher Cost: Due to their complex design, FPCs require more materials and time to produce, and are therefore generally more expensive than FFCs.
Limited Reusability: The circuits within each FPC are designed for a specific purpose and can therefore only be reused in projects that require the same functionality.
High Design Complexity: Compiling an FPC with advanced circuit patterns can take a long time to complete.
Common uses of FPC:
Smartwatches: Due to their flexible construction and advanced functionality, FPCs are used in smartwatches for features such as real-time health statistics collected from sensors.
Satellite solar panels: Inside satellites deployed into outer space, FPCs are used to connect solar panels to the satellite’s power management system. Being lightweight, they help avoid excess fuel consumption due to added weight.
Consumer electronics: FPCs are used in smartphones, tablets, laptops, and cameras, where space constraints and flexibility are critical.
Automotive: FPCs are used in complex automotive components and systems such as dashboard controls, infotainment systems, and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS).
Medical devices: In the medical field, FPCs are used in diagnostic equipment, wearable health monitors, and imaging systems.
Aerospace and defense: Due to their lightweight construction, FPCs are incorporated into aerospace navigation systems, communication equipment, and control panels.
Industrial equipment: FPCs are often used in advanced equipment such as robotics, automation systems, and complex machinery.
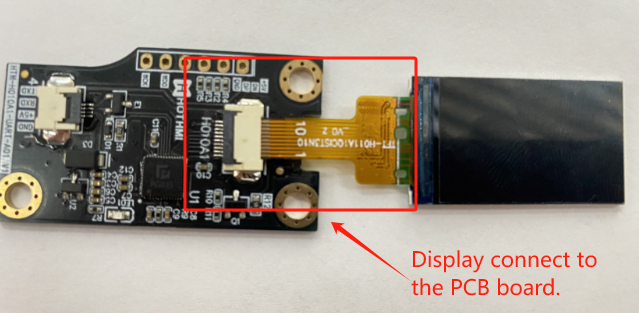
(FPC作为显示屏和驱动电路板的应用)
Hot Display's displays can also be customized with FFC connectors according to customer needs. Please contact us directly for more information!
Next article: The difference between FPC and FFC
Related Articles: What is the best way to connect the COG display to the driver board?
What are the connection methods between LCD display and PCB board?